Athletes require a well-balanced diet to fuel their bodies, enhance performance, and recover effectively. Understanding the essential nutrients that contribute to an athlete’s overall health is crucial for optimizing performance and maintaining peak physical condition. This guide explores the essential nutrients for athletes in 2024 and how to incorporate them into a balanced diet.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
1. Proteins: Building Blocks for Muscle Repair
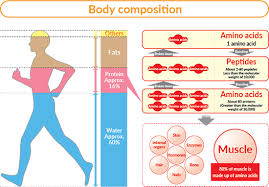
Proteins are vital for muscle repair, growth, and overall recovery. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscle tissue. For athletes, ensuring an adequate protein intake is crucial for repairing muscle damage and enhancing performance.
Sources of Protein:
- Lean Meats: Chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and mackerel.
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, milk, and cheese.
- Plant-Based: Lentils, chickpeas, tofu, and quinoa.
Daily Recommendation: Aim for 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, depending on the intensity and type of exercise.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
2. Carbohydrates: The Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for athletes, especially during high-intensity workouts. They are stored in muscles as glycogen and are used for sustained energy throughout exercise.
Sources of Carbohydrates:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread.
- Fruits: Bananas, apples, and berries.
- Vegetables: Sweet potatoes, carrots, and leafy greens.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas.
Daily Recommendation: Carbohydrate needs can vary but generally range from 5 to 7 grams per kilogram of body weight, based on the intensity and duration of the activity.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
3. Fats: Essential for Hormone Production and Energy
Fats play a crucial role in hormone production, energy storage, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. While fats are calorie-dense, choosing the right types can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and health.
Sources of Healthy Fats:
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds.
- Oily Fish: Salmon and sardines.
- Olive Oil: A great source of monounsaturated fats.
Daily Recommendation: Healthy fats should make up about 20-35% of your total daily caloric intake.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
4. Vitamins and Minerals: Essential for Metabolic Function
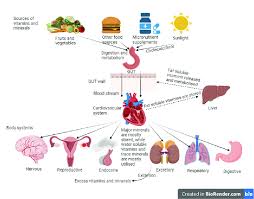
Vitamins and minerals are critical for various bodily functions, including energy production, immune function, and bone health. Athletes need to ensure they are getting a wide range of vitamins and minerals to support their intense physical activity.
Key Vitamins and Minerals:
- Vitamin C: Supports immune function and helps in collagen production (found in citrus fruits and bell peppers).
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health (found in fatty fish and fortified dairy products).
- Calcium: Vital for strong bones (found in dairy products and leafy greens).
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport (found in red meat, beans, and spinach).
Daily Recommendation: Consult with a nutritionist to determine specific vitamin and mineral needs based on your diet and exercise regimen.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
5. Hydration: Maintaining Fluid Balance
Proper hydration is essential for optimal athletic performance. Water helps regulate body temperature, transport nutrients, and remove waste products. Dehydration can impair physical performance and lead to fatigue.
Hydration Tips:
- Drink Water: Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, more if you are sweating heavily.
- Electrolytes: Include electrolyte-rich drinks or foods like coconut water, bananas, and sports drinks during prolonged exercise.
- Monitor Urine Color: Light yellow indicates good hydration, while dark yellow suggests you need more fluids.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
6. Meal Timing: Optimizing Performance and Recovery
Meal timing can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and recovery. Eating the right nutrients at the right times helps maintain energy levels and supports muscle repair.
Pre-Workout:
- Meal: A balanced meal with carbohydrates and protein 2-3 hours before exercise.
- Snack: A small snack with easily digestible carbs and protein 30-60 minutes before exercise.
Post-Workout:
- Meal: A meal rich in carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to 2 hours after exercise.
- Snack: A recovery snack with protein and carbs to replenish glycogen stores and repair muscles.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
7. Supplements: Enhancing Athletic Performance

While a balanced diet should be the primary source of nutrients, some athletes may benefit from supplements to meet specific needs or enhance performance.
Popular Supplements:
- Protein Powders: Whey, casein, or plant-based protein powders for muscle repair and growth.
- Creatine: Supports increased strength and muscle mass.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): Aid in muscle recovery and reduce soreness.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Support overall cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation.
Note: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
<!– Replace with an actual image URL –>
Conclusion
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is key for athletes looking to optimize their performance and recovery in 2024. By focusing on proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, hydration, and proper meal timing, athletes can ensure they are fueling their bodies effectively. Incorporate these guidelines into your daily routine to enhance your training results and overall health.



